|
|
| |
INTRODUCTION
This essay will explain some aspects of the national debt giving the meaning of public debt and explaining the disadvantages of a large debt. I will also describe how the British government financed the national debt in the 1700s throw the proposed of the South See Company.
THE NATIONAL DEBT
National debt
The budget deficit, the excess of central government's spending over its tax receipts, refers to the debt that the government incurs in one year. If the administration runs persistent deficits over many years, these debts will accumulate. The accumulated debt is known as the national debt.
We have to note that the national debt is not the same thing as the
country's overseas debt. Only a relatively small fraction of the national debt
is owed overseas. The bulk of it is owed to (
In other words, the government finances its budget defi 737i87h cits largely by borrowing at home and not from abroad. So the nation's trade deficit is equal to the imbalance between national investment and national saving.
Government debt can be divided into:
o Internal debt, owed to lenders within the country;
o External debt, owed to foreign lenders.
The debt consists of government bonds, bank loans, and according to some measures, unfunded liabilities such as pension plan payments and goods and services the government has contracted for but not yet paid.
Another common division of government debt is by duration:
o Short term debt is generally considered to be five years or less;
o Medium term debt falls between short and long term;
o Long term is more than ten years.
The size of the deficit or surplus will depend on the state of the economy. If the economy is booming with people earning high incomes, the amount paid in taxes will be high. In a booming economy the level of unemployment will be low. Thus, the amount paid out in unemployed benefits will also be low.
The combined effect of increased tax revenues and reduced government expenditure is to give a public-sector surplus.
By contrast, if the economy was depressed, tax revenues would be low and government expenditure on benefits would be high.
The debt, as I have mentioned before, is owed to a number of
sources. For example, individual Americans and businesses buy savings bonds and
T-bills. Much of the debt is held overseas, however. This is especially true of
However, the size of the deficit or surplus, tell us very little about whether the economy will expand or contract.
Reasons for Government Indebtedness
Governments may borrow to meet temporary needs, as when estimated revenue falls below or is exceeded by estimated expenditures. Short-term treasury notes, payable by increased taxes or by greater economizing, may be issued, but such a debt should not become permanent. Nonetheless, many national governments incur such debt because of an unwillingness to limit spending or increase taxes for fear of the political consequences. Borrowing to finance public works, especially when widespread unemployment exists, is another source of public debt and is justified in part by their long-term social utility. The largest public debts are incurred to meet emergencies, such as war debts that arise when it is difficult to finance the extended activities of the government by new or increased taxes, or when the government must borrow abroad to finance the war effort.
Public debt is advantageous in that part of the national funds are secured at an interest rate lower than that provided to private industry and in that the financial operations of government are funded on a permanent basis. It may also have an expansionary effect on employment and production during times of high unemployment.
The disadvantages are that unjustifiable projects may be undertaken because the full burden of payment is postponed; that the government's demands may become so large that the interest rate on government bonds will rise to the point where money is diverted from private enterprise; and that too great a debt may induce governments to depreciate currency or default on obligations.
In the dominant economic policy generally ascribed to theories of John Maynard Keynes, sometimes called Keynesian economics, there is tolerance for quite high levels of public debt to pay for public investment in lean times, which can be paid back with tax revenues that rise in the boom times.
As this theory gained popularity in the 1930s globally, many nations took on public debt to finance large infrastructural capital projects or large hydroelectric dams. It was thought that this could start a virtuous cycle and a rising business confidence since there would be more workers with money to spend and this would have helped the world economies to gain traction to exit the Great Depression. However, this was not true, as it was only the military spending of World War II that really ended the Great Depression.
Initial stages, France
In the 1700s we sow a revolution in the World's economy with the
foundation of what it was called "new economy". In fact during this century,
and in the following years, we have the introduction of paper notes, Stock
Exchanges, banks and the creation of some economics theory. All begun in
"The government in
The government believed that "
o "£18.3m was held by 3 large corporations:
£3.4m by the Bank of
£3.2m by the British East India Company;
£11.7m by the South Sea Company.
o Privately held redeemable debt amounted to £16.5m.
o £15m consisted of irredeemable annuities, long fixed-term annuities of 72-87 years and short annuities of 22 years remaining maturity."
(From: https://en.wikipedia.org)
From this instable situation a men, called John Blunt kept advantage. Drawing on a similar scheme run in France by Law, Blunt's scheme involved buying the national debt off the government and then selling it to investors through the issue of shares on the basis of £100 of equity for £100 of debt.
He then persuaded the government's creditors to exchange their
annuities for
So, as the bubble mania got underway, Blunt only needed to issue a single £100 share to redeem £1,000 of annuities. As long as shares went up and up it seemed like a perpetual motion machine for making money.
Blunt understood human nature and human ignorance, and used the two great pillars of insatiability and credulity to launch the first pure example of what has since become the classic form of capitalist fraud: company promotion. So long as he could persuade his contemporaries that the share price would raise, cash would pour into the company in limitless amounts in exchange for new shares, and the holders of government debt would convert their incomes into worthless paper. The national debt, or much of it, was thus first "equalised" and then, when the smash came, effectively liquidated.
The share price kept going up and so many annuitants cashed their government stock into shares, helped by loans from the company and bribes that the South Sea Company ended up controlling half the government debt.
At its peak the South Sea Company was valued at 10 times the size of the national debt it was holding while its ships had not sailed anywhere near the South Seas.
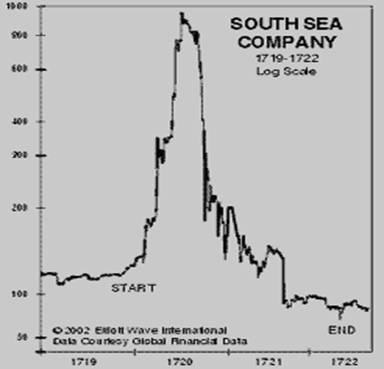
South See Co. graph 1719/1722
(From: www.stock-market.net)
CONCLUSION
I believe that a State which is running a very high national debt is actually borrowing from the future. This is true because in order to finance their excess expenditure, governments will need to issue new bonds or collect more taxation to finance their debt and the matured securities. Those new bonds will be bought by future generations and those higher taxes will be imposed on future generations. It is a bit like the consumer who increases its mortgage on his house to finance his lifestyle: he or his sons will eventually have to repay it.
Irrationality is an aspect of human psychology. The South See Bubble was the first example of it. During the centuries many other bubbles developed and eventually busted. Most recently the Dot.com and telecom bubbles are good examples of this irrational behaviour. Some economists and government officials are arguing that the next big bubble will be that of the American Consumer and their overvalued houses. So far things have been holding up quite well also thanks to a very low interest rate policy from the Federal Reserve. Time hold the ultimate answer to this dilemma. We cannot do anything but keep our borrowing low and wait and see.
Word count: 1543
BIBLIOGRAPY
Books:
Balen, M. (2003) A very English Deceit, Fourth Estate
Vaitilingam, (2001) Using the Financial Pages, Pentice Hall
Lipsey & Chrystal, (1991) Economics, 3rd
edition,
Web:
www.stock-market.net
|
Privacy |
Articolo informazione
Commentare questo articolo:Non sei registratoDevi essere registrato per commentare ISCRIVITI |
Copiare il codice nella pagina web del tuo sito. |
Copyright InfTub.com 2025